MERRY CHRISTMAS FROM OUR FAMILY TO YOURS
It’s December! Bring on all the end-of-year celebrations after another great year. How are you celebrating and acknowledging the last 12 months?
End of Year Celebrations
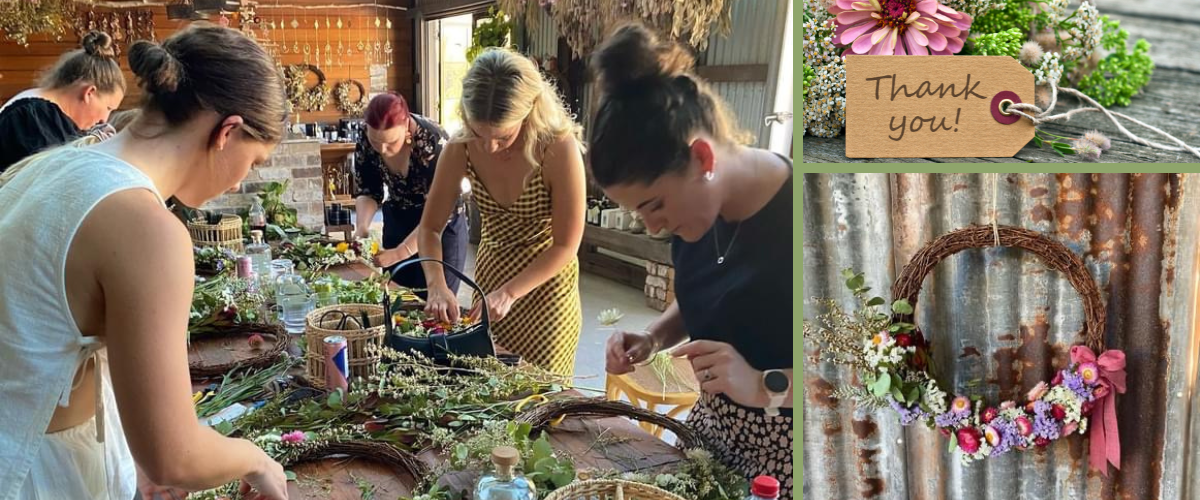
For us, our team have been all together again in November and have had our Christmas Party. We celebrated the last year by being creative with making Christmas wreaths, eating delicious foods and spending some quality time together. Check out some of our Christmas celebratory pictures. Lots of laughs were had!
We have continued our time together to participate in a team day, where we have spent time together reflecting on just how much we have achieved together for ourselves, clients, their families and our communities. We have been beyond grateful to continue sharing our knowledge and providing ongoing support, therapy and guidance in achieving your goals this year. So, thank you for being vulnerable and safe in allowing us to come into your home and work so closely to gain these achievements! Without your ongoing commitment, we wouldn’t be able to work so effortlessly alongside you!!
This opportunity has also allowed us to identify where we will focus on for 2024. As you know, we love a good theme, and this coming year, we have another coming your way. Keep an eye out for our New Year January blog, where we will share the 2024 Annual Theme and all the new exciting things coming!
School Holiday Groups & Intensives!
The last 12 months, we have been focused on developing new group programs for our clients based on feedback we have received. We have been working behind the scenes to be able to offer these options for January 2024. It gave us such joy to announce and share them with you all. If you have missed out on seeing these groups, make sure you check out our website for all the information or contact us today!
These new group programs, “Game Changers” and “Transition to High School”, will commence in the January 2024 school holidays alongside our popular group programs “Big School STARS (transition to Kindergarten)”, “Shake n Bake” and “Teenage Dirtbags”.
Based on our group numbers, we will also offer limited spots for our School Holiday Intensives Programs. If you would like the opportunity to commence the year strong, discuss it with your treating clinician or call our office today.
Merry Christmas & Happy New Year!
With great love and well wishes, the Explore and Soar team wishes you a great end of year with lots of celebrations, rest and family time. We look forward to going on a well-deserved break with you all from Friday, 15th December 2023 and returning on Monday, 8th January 2024.
We can’t wait to see you all in 2024.
Until next time,
Jess